Relevance
As a central component of Māori culture, Māori language is an important aspect of participation and identity. The Māori language forms part of the broader cultural identity and heritage of New Zealand and in 1987 was granted the status of an official language of New Zealand.71
Current Level
The 2001 Census showed that one-quarter of all Māori (25 percent or 130,482 Māori) and 28 percent of Māori aged 15 and over (or 91,809) stated they could hold a conversation in Māori about everyday things. Māori accounted for 81 percent of the total number of Māori language speakers (160,500). The 1996 Census also showed that the proportion of Māori who speak te reo was around 25 percent, but because of changes in the census ethnicity measures this figure is not directly comparable with the figure for 2001.
The proportion of Māori who were fluent Māori speakers declined markedly over the last century, particularly following the rapid urbanisation of the Māori population in the 1950s and 1960s. The first national Māori language survey in 1973 estimated that the proportion of fluent speakers had fallen to 18 percent.
Information on the fluency of Māori speakers is available from the survey of the health of the Māori language, conducted in 2001. The survey showed that more people could understand Māori (59 percent of Māori aged 15 years and over, or 190,209) than speak it (42 percent, or 136,600). In terms of proficiency, while 42 percent could speak some Māori, only 9 percent could speak Māori 'well' or 'very well', 11 percent could speak Māori 'fairly well', and 22 percent could speak Māori but 'not very well'. Similarly, while 59 percent of people could understand Māori, only 15 percent could understand Māori 'well' or 'very well', 18 percent could understand Māori 'fairly well', and 25 percent could understand Māori but 'not very well'.72
Figure CI2.1 Proportion of Māori
speakers in the Māori population by age & sex, 2001
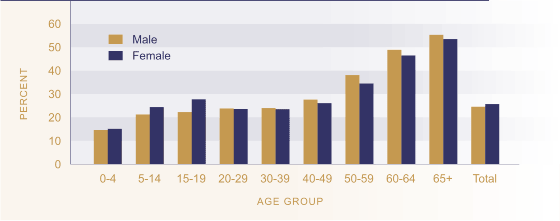
Source: Statistics New
Zealand 2001 Census
Age And Sex Differences
Older Māori are considerably more likely than younger Māori to be able to converse about everyday things in Māori. In the 2001 Census, more than half of Māori aged 65 and over (54 percent) reported having conversational fluency in the Māori language, compared with less than one-quarter (22 percent) of Māori under 40.
Sex differences in the proportion of Māori language speakers were also apparent. From age 40 years onwards, males were more likely than females to be Māori language speakers, while at younger ages (below 20 years) a higher proportion of females than males could speak Māori.
Among non-Māori, the proportion of Māori language speakers was higher at the younger ages. Females were also more likely to be Māori language speakers than males.
Ethnic Differences
The 2001 Census showed that 4.5 percent of the total population could hold a conversation in Māori. After Māori, Pacific peoples had the highest proportion who could speak Māori (5.8 percent), followed by Europeans (1.7 percent) and Asians (0.8 percent).
Regional Differences
Māori who live in areas with a high proportion of Māori residents are the most likely to be Māori language speakers. Regions with the highest proportion of people with conversational Māori skills were Gisborne (35 percent), Bay of Plenty (32 percent), Northland (30 percent), Waikato (28 percent) and Hawkes Bay (27 percent).
