Voter turnout
Definition
General elections: The proportion of the estimated voting-age
population (aged 18 and over) who cast a valid vote in general elections.
Local authority elections: The proportion of all enrolled electors (both
resident and ratepayer) who cast a vote in contested local authority elections.
Relevance
Voter turnout rates are a measure of political participation.
They can be seen as an indicator of the extent to which citizens are a
part of the political process, and the confidence the population has in,
and the importance they attach to, political institutions.
Current level and trends
1. General elections
Voter turnout of the eligible
population was 72.5 percent in 2002. Voter participation in general elections
declined sharply from 89 percent in 1984 to 78 percent in 1990, increased
slightly to 81 percent in 1996, then declined again to a new low in 2002.
Figure CP1.1 Proportion of estimated voting-age population
who casts votes, 1984–2004
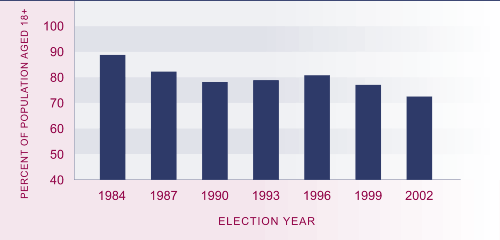
Source: Electoral Commission (2002)
p174. 1984 figure calculated by the Ministry of Social Development
Comparisons between groups
Because of the nature of the secret ballot,
information on differences in participation rates among various sectors of the New Zealand population is not directly available. Nevertheless, results from New Zealand election surveys over a number of years associate several social, demographic
and occupational characteristics with impacts on the voter turnout rate.
Non-voters are more likely to be people on lower incomes, younger people
and members of Māori or Pacific ethnic groups. There are few differences
in voting turnout rates between men and women.
Regional differences
There are few discernible differences
in voting turnout rates between rural and urban voters, although non-voting tends to be
lowest in provincial cities.
International comparison
New Zealand's voter turnout rate in 2002
was 72.5 percent, compared to an OECD median of 71 percent over 1997–2002.67 This
placed New Zealand 15th out of 30 OECD countries. Greece had the highest
voter turnout at 89 percent. Voter turnout was higher in Australia (sixth,
82 percent) than New Zealand, but lower in the United Kingdom (23rd, 58
percent), Canada (26th, 55 percent) and the United States (29th, 47 percent).
Current level and trends
2. Local authority elections
There are 253 elected local authorities
in New Zealand : 12 regional councils, 21 district health boards (established 1 January 2001), 15 city councils, 59 district councils and 146 community boards. There was
a major restructuring of local government in 1989.
Voter turnout in the 2001 local authority elections was the lowest
since 1989 for all, except regional councils, which had the second lowest
since then.
Table CP1.1 Voter turnout (%) in local authority elections, 1989–2001
| |
1989 |
1992 |
1995 |
1998 |
2001 |
| Regional
councils |
56 |
52 |
48 |
53 |
49 |
| District
health boards |
- |
- |
- |
- |
50 |
| Territorial authorities |
|
|
|
|
|
| City
councils |
52 |
48 |
49 |
51 |
45 |
| City
mayors |
50 |
48 |
49 |
51 |
45 |
| District
councils |
67 |
61 |
59 |
61 |
57 |
| District
mayors |
67 |
61 |
59 |
59 |
56 |
| Community
boards |
54 |
49 |
50 |
50 |
46 |
Source: Department of Internal Affairs
(2003) Table 7.1
Note: There was no election held for Rodney District in 2001
Local authority voter turnout is generally highest for district
councils, with their more rural population base, for smaller city councils
and for councils in the South Island. These councils all had a majority turnout in 2001, while among large city councils
and North Island city councils, fewer than half of the eligible electors
voted. Voter turnout ranged from 65 percent for district councils in the
South Island to 43 percent for city councils in the North Island.
In large regional councils, there was an upward trend in voter
turnout between 1995 and 2001. However, the average turnout was still higher
among small regional councils. Similarly, voter turnout was highest on
average among the smaller district health boards.
|

