People
The social report monitors outcomes for the New Zealand population. This section contains background information on the size and characteristics of the population to provide a context for the indicators that follow.
Population size and growth
New Zealand’s resident population reached 4 million in 2003 and was estimated to be 4.25 million at the end of December 2007.
During 2007, the population grew by 41,200 or 1.0 percent. This rate of growth was lower than that recorded in 2006 (50,400 or 1.2 percent) and lower than the average annual increase during the decade ended December 2007 (45,000 or 1.1 percent).
Under 2006-based medium population projection assumptions, the population growth rate is expected to drop from 1.0 percent in 2007 to 0.9 percent by 2011. Natural increase will account for three-quarters of this growth, and net migration the remaining quarter. Assuming net migration of 10,000 people per year after that, the growth rate is expected to slow to 0.7 percent per year between 2021 and 2026. Such a growth rate would add around 711,500 people to the population between 2007 and 2026.5
Figure P1 Estimated and projected resident population, 1991–2026
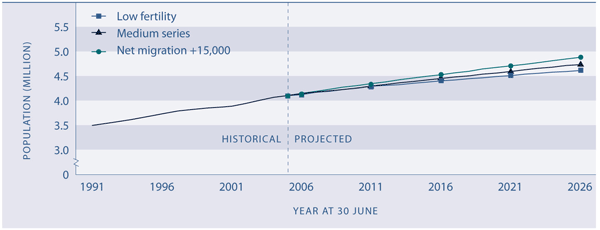
Source: Statistics New Zealand
Note: All three projection series assume medium mortality (life expectancy at birth 84.5 years for males, 88.0 years for females by 2061).
The low fertility series (total fertility rate of 1.7 births per woman by 2026) and the medium series assume a long-term annual net migration gain of 10,000 from 2010. The medium series and the high migration series assume medium fertility (total fertility rate of 1.9 births per woman) |

